Table of Contents
Understanding Diffusion
Diffusion is the process by which molecules spread from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration. This movement continues until equilibrium is reached, meaning that the concentration of molecules becomes uniform throughout the space. Diffusion can occur in gases, liquids, and even solids, and it plays a crucial role in various biological and chemical processes.
One common example of diffusion is the way a drop of food coloring disperses in water. Initially, the color is concentrated in one area, but over time, it spreads out evenly throughout the liquid. This natural tendency of molecules to move towards areas of lower concentration drives many essential functions, such as gas exchange in the lungs and nutrient absorption in cells.

Exploring Osmosis
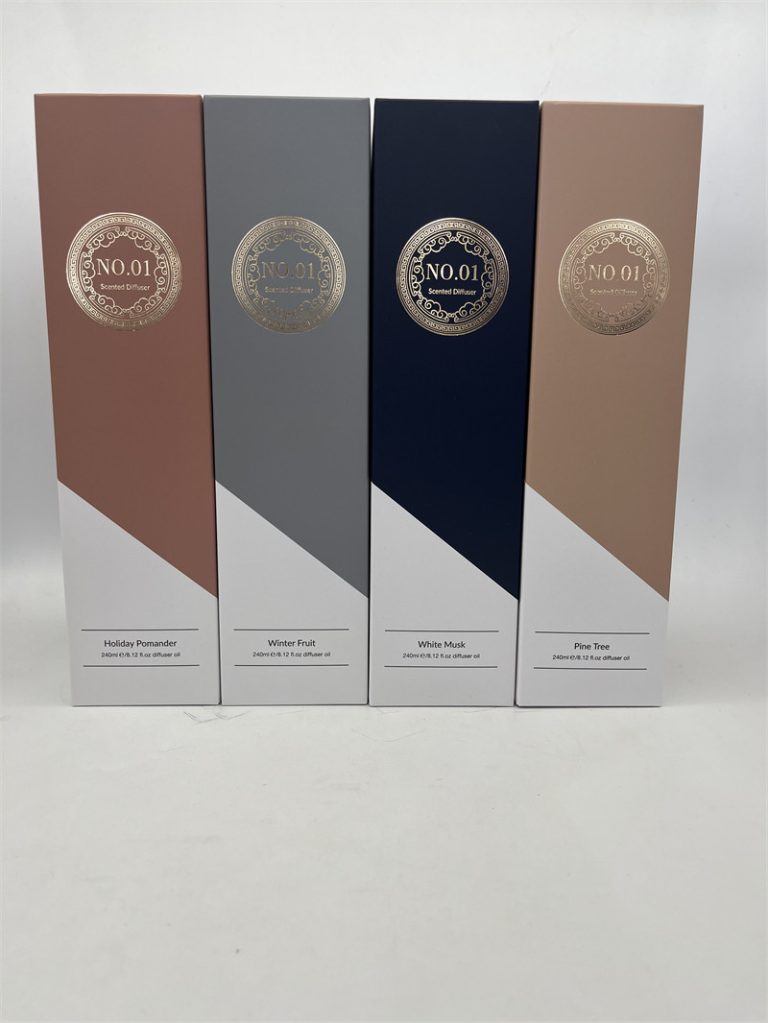
| Article Name | Room Diffuser |
| Material | Metal |
| Suitable for | Office |
| Scents | Rose & Violet, Sun Glow |
| Capacity | 400ml |
| Color | Silver |
| Origin | China Company |
| Duration | 1 year |
https://reedaromalab.com/tag/high-grade-reed-oil-diffuser-supplier
Osmosis is a specific type of diffusion that pertains to the movement of water molecules through a selectively permeable membrane. Unlike general diffusion, which can involve various types of molecules, osmosis specifically focuses on the movement of water. Water moves from an area of low solute concentration to an area of high solute concentration, aiming to equalize solute concentrations on both sides of the membrane.
This process is vital for maintaining cell turgor pressure and overall homeostasis in living organisms. For instance, when plant roots absorb water from the soil, osmosis plays a key role in drawing water into the roots, which is essential for the plant’s survival. Additionally, osmosis is involved in kidney function, where it helps regulate the concentration of urine.
Key Differences Between Diffusion and Osmosis
While diffusion and osmosis are both passive transport processes that involve the movement of molecules, they differ primarily in terms of what substances are being transported and the presence of a membrane. Diffusion can involve any type of molecule, whereas osmosis specifically concerns water molecules. Furthermore, osmosis requires a selectively permeable membrane, which allows only certain substances to pass through, while diffusion does not necessitate such a barrier.
Another important distinction is the direction of movement. In diffusion, molecules move from areas of higher concentration to lower concentration until equilibrium is achieved, regardless of the presence of a membrane. In contrast, osmosis involves water moving toward higher solute concentrations, which may not always correlate with the overall concentration gradients of other substances.