Table of Contents
Understanding Wick Materials
Wicks are a crucial component in candle making, influencing not only how well a candle burns but also its overall safety and performance. The choice of wick material can significantly affect the candle’s burn rate, scent throw, and even how the wax melts. Common wick materials include cotton, wood, and synthetic fibers, each offering unique characteristics that candle makers should consider.
Cotton wicks are the most widely used option due to their reliability and ease of use. They typically come pre-waxed and have a consistent burn rate, making them suitable for various types of candles. Additionally, cotton wicks can be braided or twisted, allowing for different thicknesses and sizes depending on the candle design. This versatility makes cotton a favorite among both beginners and experienced candlemakers.
Wooden wicks have gained popularity in recent years due to their aesthetic appeal and unique burning characteristics. When burned, wooden wicks produce a soft crackling sound reminiscent of a fireplace, adding to the ambiance of the candle. They tend to burn hotter than cotton wicks, which can enhance scent throw, but they may require more careful sizing and placement to ensure an even burn.
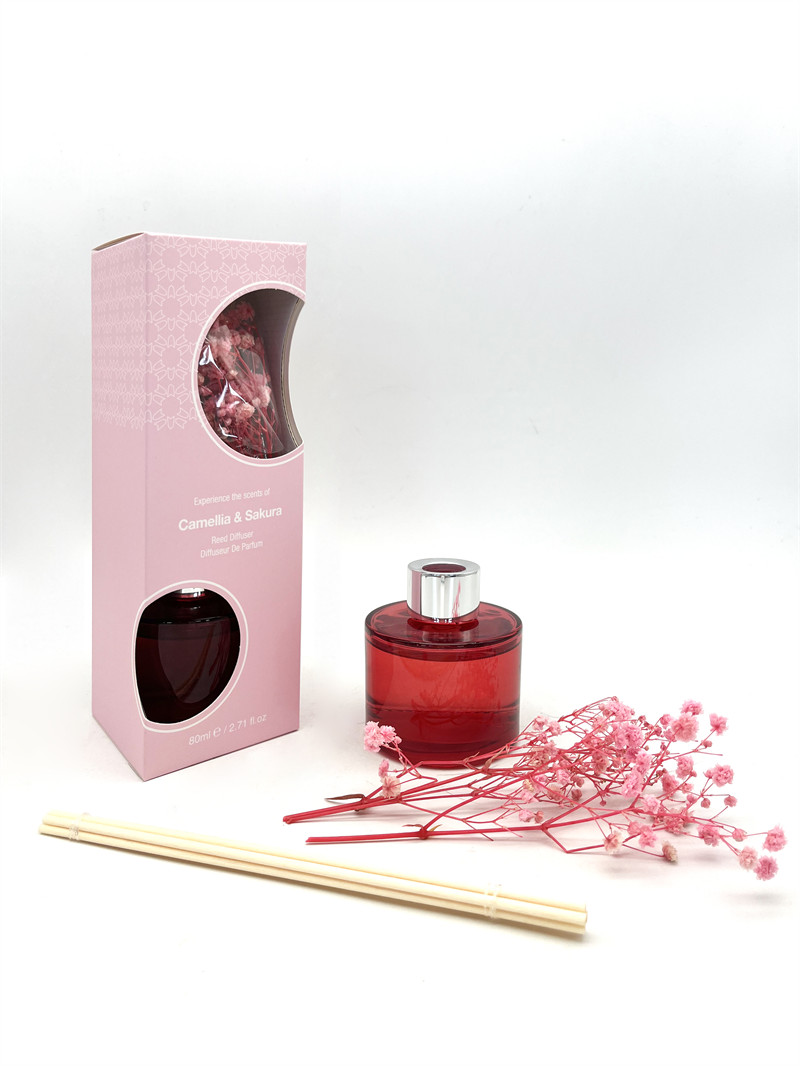

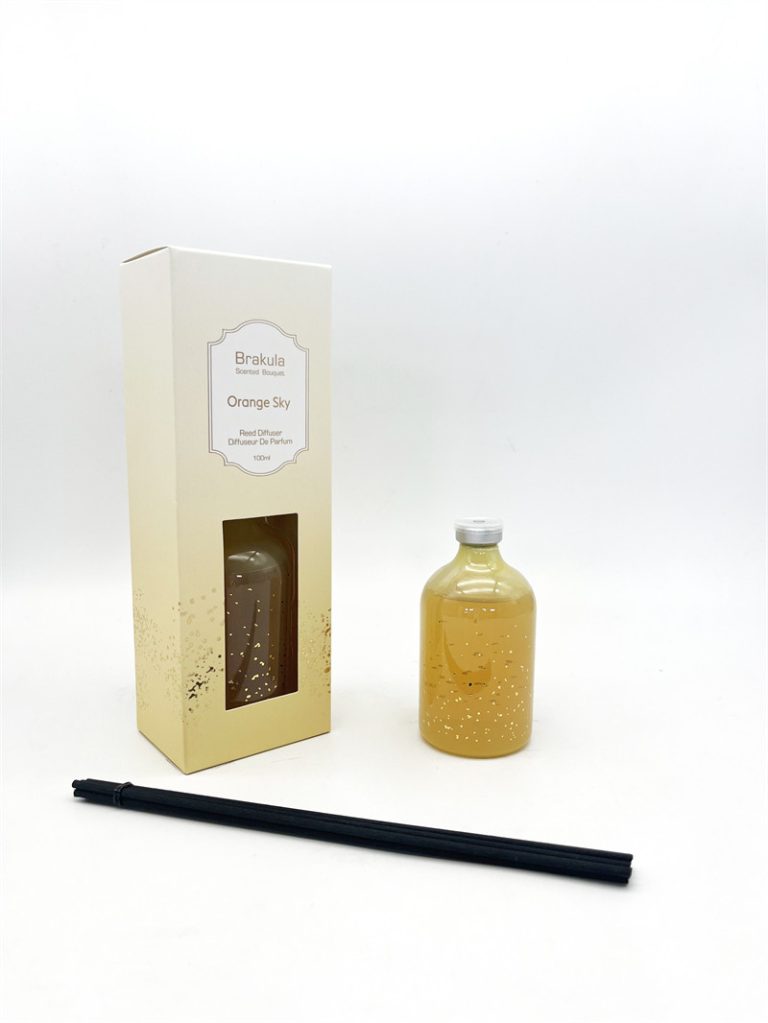
| Products | Room Fragrance |
| Material | Ceramic |
| Suitable for | Toilet |
| Scents | Fresh Cotton, Orange Lily |
| Capacity | 400ml |
| Color | Orange |
| Origin | China Company |
| Duration | Customizeds |
Choosing the Right Wick for Your Candle
When selecting the best wick material for your candle, it is essential to consider the type of wax you are using. Different waxes, such as paraffin, soy, or beeswax, may react differently with various wick materials. For example, soy wax often works best with cotton wicks, as they provide a steady flame and support proper melting. Conversely, certain types of beeswax candles may benefit from wooden wicks due to their higher burn temperature.
Another factor to consider is the diameter of the candle. A larger diameter candle may require a thicker wick to maintain a sufficient melt pool and prevent tunneling. In contrast, a smaller diameter candle might need a finer wick to avoid excessive soot or overburning. Testing different wick sizes and materials is often the best approach to find the perfect match for your specific candle formulation.
Finally, it’s important to experiment with wick treatments and additives. Some candlemakers choose to coat their wicks with a blend of wax or fragrance oils to enhance performance. Others may dip their wicks in certain solutions to improve burn stability. Each of these variables can impact how a candle burns, so keep detailed notes of your experiments to refine your process over time.
https://reedaromalab.com/tag/high-quality-room-fragrance-wholesale-price